Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

Because the membrane is fluid and because of the mosaic arrangement of the protein molecules the structure of the membrane.
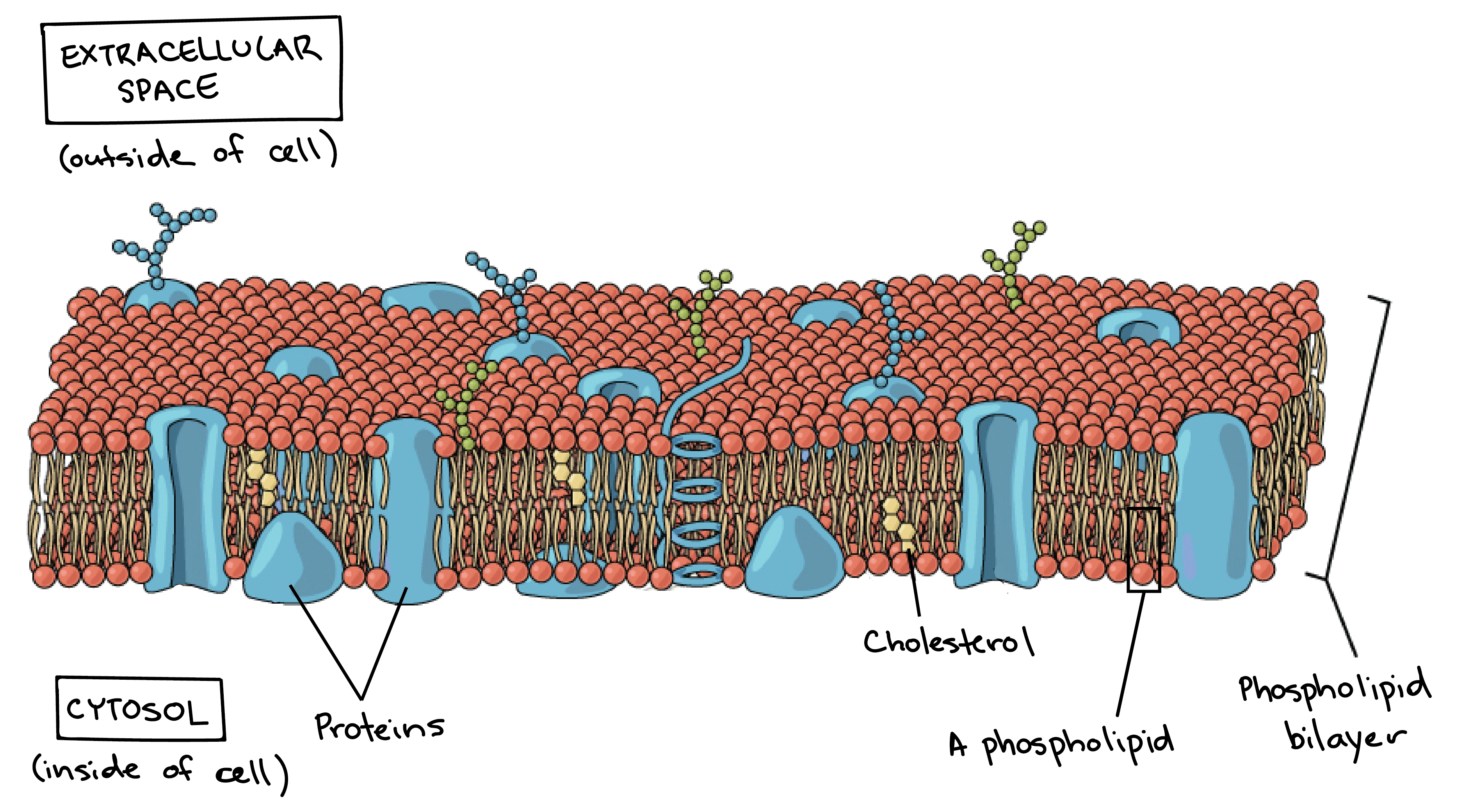
Cell membrane structure and function a level. Scanning electron micrograph SEM of adipocytes Ad Membrane Structure and Function Prokaryotic Cells. Much of the membrane is made up of a sea of phospholipids with protein molecules floating in between the phospholipids. This is a thin flexible layer round the outside of all cells made of phospholipids and proteins.
Organelles perform different functions within a cell and this is called the Division of Labour. The Formation of Cell Membranes is Crucial to Life. The plasma membrane cell surface membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell.
The membrane is examined in detail later. The separation of different parts of the cell with different functions by using membranes is called compartmentalisation providing distinct conditions for different processes. Thin barrier separating inside of cell cytoplasm from outside environment Function.
Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals. Many membranes within the cell help to make different compartments for different chemical reactions to take place. Membranes formed from phospholipid bilayers help to compartmentalise different regions within the cell as well as forming the cell surface membrane Exam Tip An example of a membrane-bound organelle is the lysosome found in animal cells each containing many hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many different kinds of biomolecule.
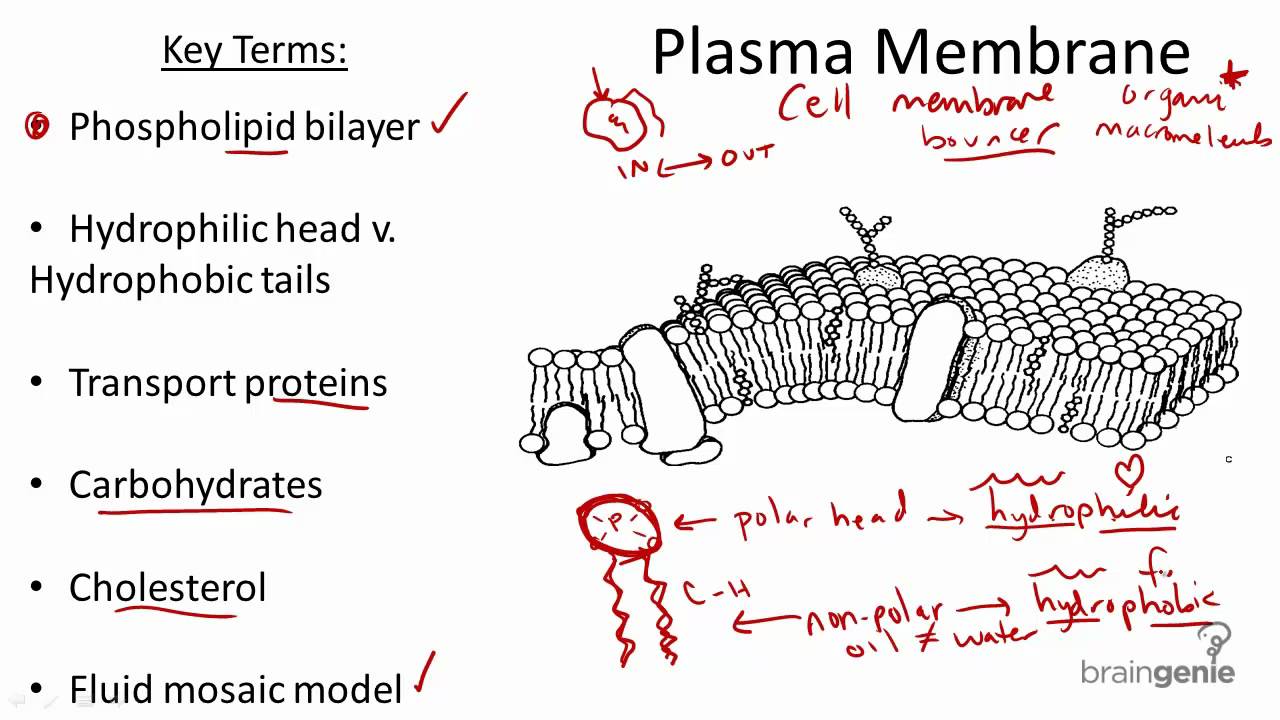
The membrane also contains membrane proteins including integral proteins that go across the membrane serving as membrane. All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes and this characteristic best portrayed by the Fluid Mosaic ModelAccording to this model which was postulated by Singer and Nicolson during the 1970s plasma membranes are composed of lipids proteins and carbohydrates that are arranged in a mosaic-like manner. It is a fluid mosaic of lipids proteins and carbohydrate.
In plant cells the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. Formed from a phospholipid bilayer with the hydrophobic tails pointing towards each. Form the basic structure of the membrane phospholipid bilayer The tails form a hydrophobic core comprising the innermost part of both the outer and inner layer of the membrane.