Cell Membrane Structure Journal

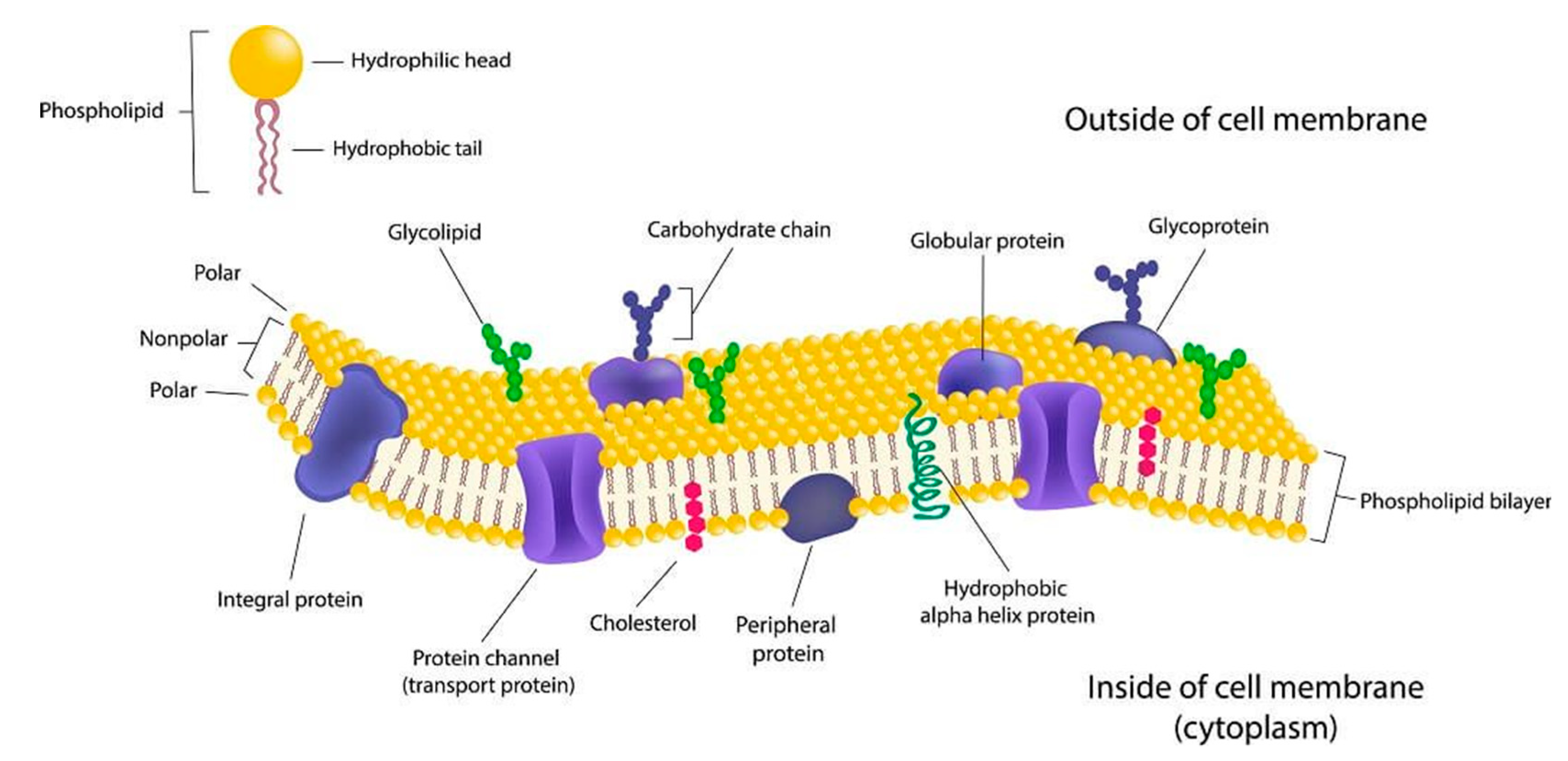
Thefluid mosaic model ofthe cell membrane.
Cell membrane structure journal. 3 in Singer S. In particular we welcome work that uses modern experimental or computational methods including but not limited to those with microscopy diffraction NMR computer simulations or biochemistry aimed at membrane associated or membrane embedded proteins or model membrane. Red Cell Antigens and Antibodies ed.
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. Updated October 07 2019. The paucimolecular unit membrane model of the structure of the plasma membrane is critically reviewed in relation to current knowledge of the chemical and enzymatic composition of isolated plasma membranes the properties of phospholipids the chemistry of fixation for electron microscopy the conformation of membrane proteins the nature of the lipid-protein bonds in membranes and possible mechanisms of transmembrane transport and membrane.
View our cryo-EM collection from Structure and Molecular Cell The papers included in the collection showcase how cryo-EM has enabled us to address SARS-CoV-2 biology antimicrobial resistance mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis the architecture and dynamics of integrator complexes ion channels receptors and phage-genome degradation versus host-genome protection. Our editorial process. 2 proteins aggregate to form islands evenly dispersed at the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane with a height of 1012 nm.
The cell membrane is a complex barrier separating every cell from its external environment. THE formation of single stable bimolecular lipid and proteolipid1 membranes up to 10 mm2 in area has been accomplished routinely in 01 M saline solution by methods analogous to the formation of. We investigate this relationship by looking for connections between cell membrane elastic properties especially surface tension and bending modulus and cell function.
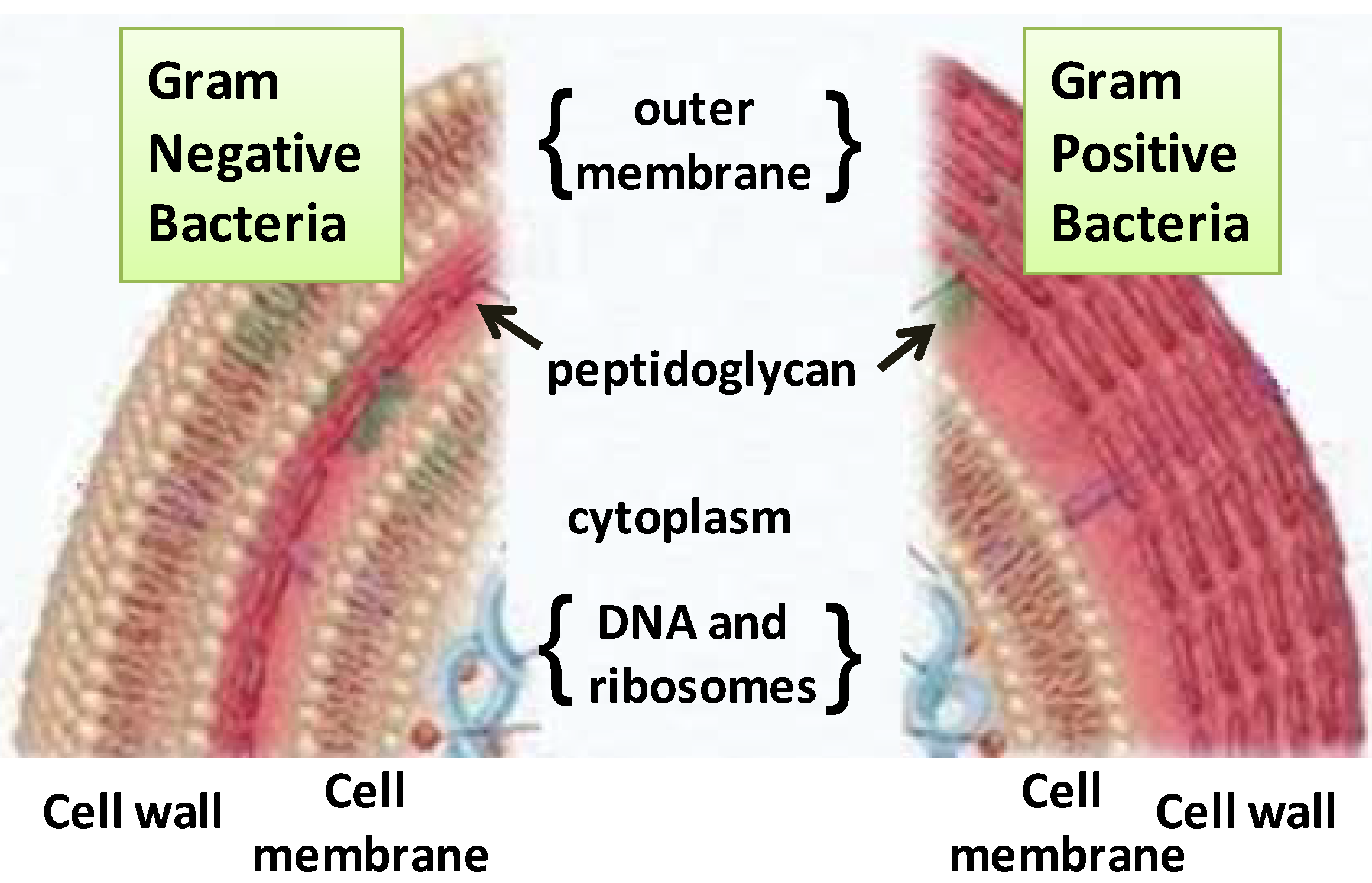
This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. This focus issue on membrane biophysics presents a collection of papers illustrating new developments in modern biophysical research on cell membranes. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
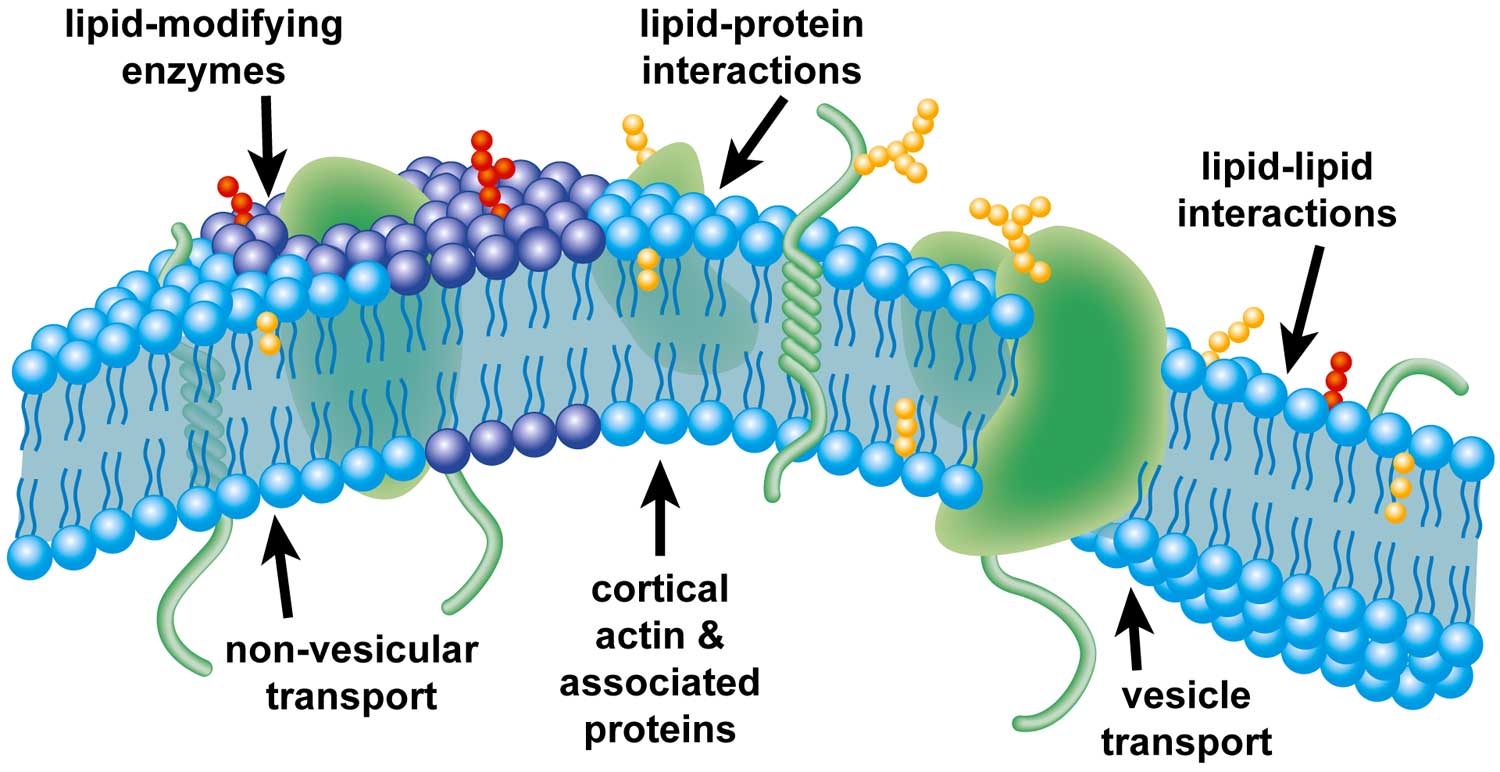
Recent studies indicate that the cell membrane interacting with its attached cytoskeleton is an important regulator of cell function exerting and responding to forces. These proteins have transmembrane domains which insert into the lipid bilayer and can form complexes with both extracellular and intracellular proteins. Considerable progress has been made in understanding the roles played by two membrane lipids.