Cellular Respiration Formula Definition

Cellular respiration is defined as the conversion of fuel into energy and nutrients within the mitochondria and cytosol of cells.
Cellular respiration formula definition. The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs where it is exchanged for oxygen. Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms convert the biochemical energy of nutrients into ATP. Cellular Respiration Definition Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy.
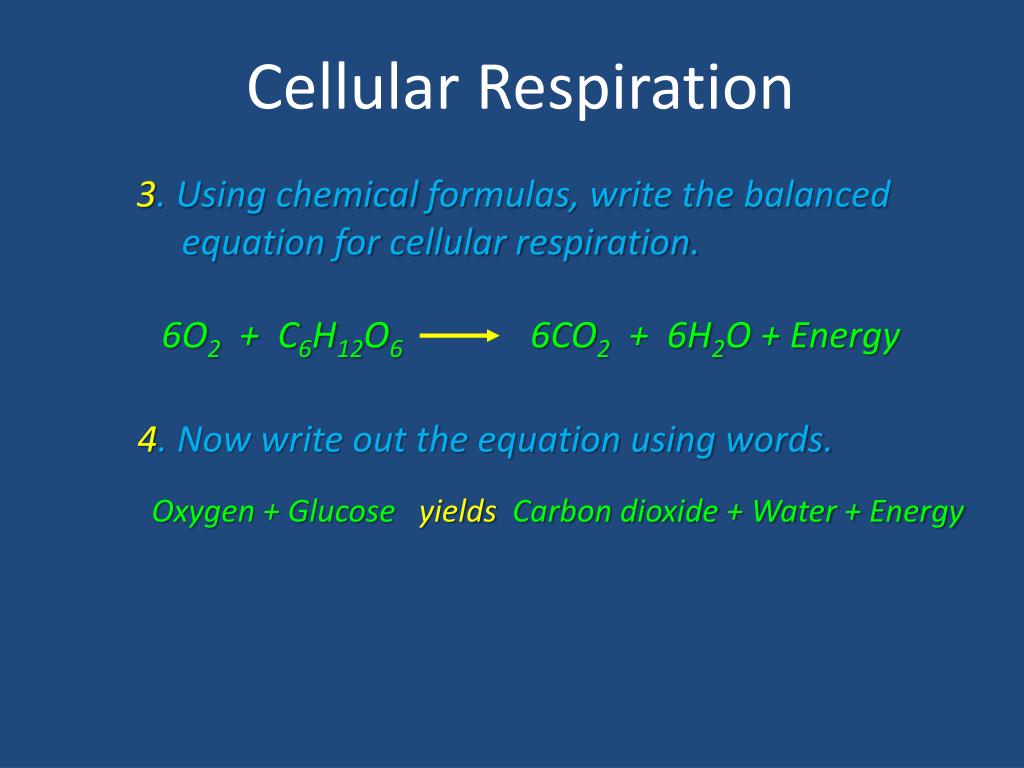
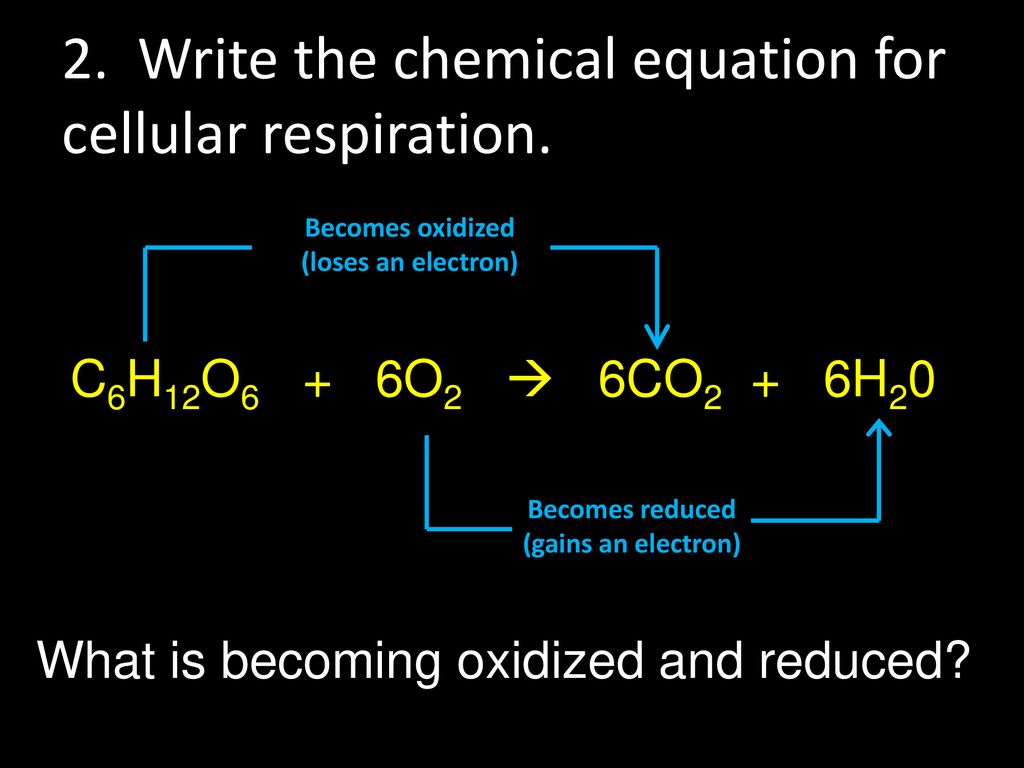
How to use cellular respiration in a sentence. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O ATP is the complete balanced chemical formula for cellular respiration.
The Purpose Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process by which cells in plants and animals break down sugar and turn it into energy which is then used to perform work at the cellular level. The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
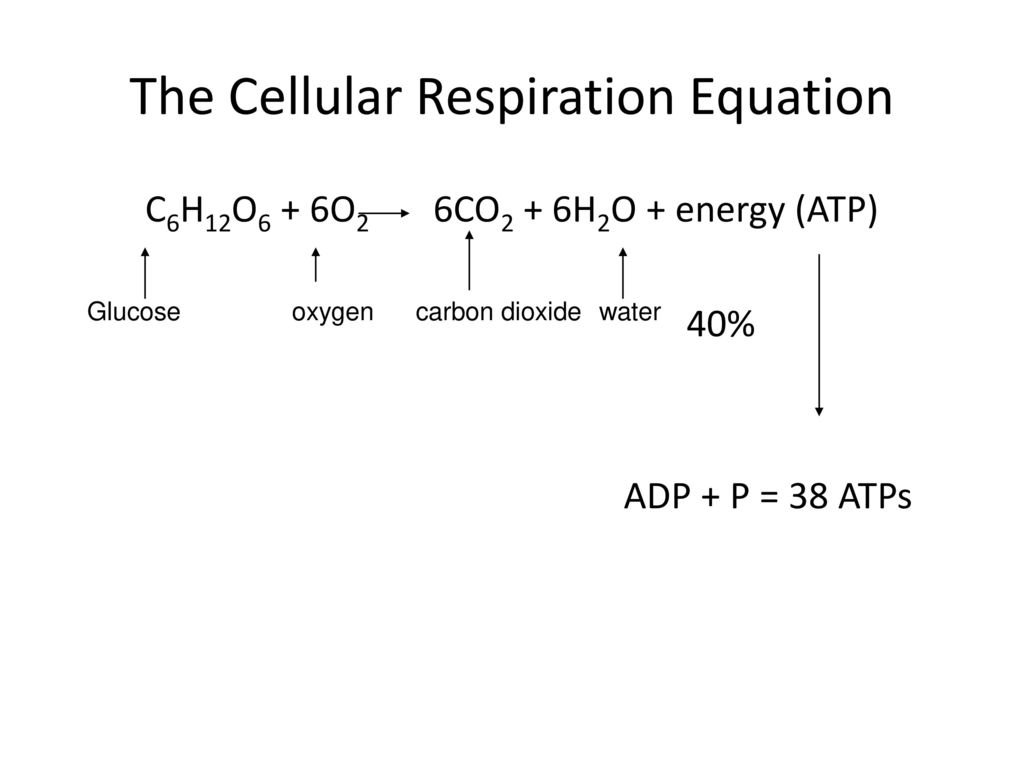
The process of breakdown of primary metabolites like glucose protein fatty acids etc in the cell with the release of energy in the form of ATP is called cellular respiration. During cellular respiration one glucose molecule combines with six oxygen molecules to produce water carbon dioxide and 38 units of atp. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a metabolic pathway Two types of cellular respiration exist.
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process consisting of a series of steps to convert chemical energy sugar into a usable form of energy ATP in the cell. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O Energy as ATP The word equation for this is. C 6 H 12 O 6 1 glucose molecule 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 36 ATP ENERGY carbohydrate oxygen carbon dioxide water ATP energy.
This process breaks down glucose into six carbon dioxide molecules and twelve water molecules. It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in all living cells to release energy by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate- ATP.