Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation.
Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy. Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides primarily ATP by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions. The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration.
Glucose and then stored in energy-carrying biomolecule eg. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in all living cells to release energy by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate- ATP. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
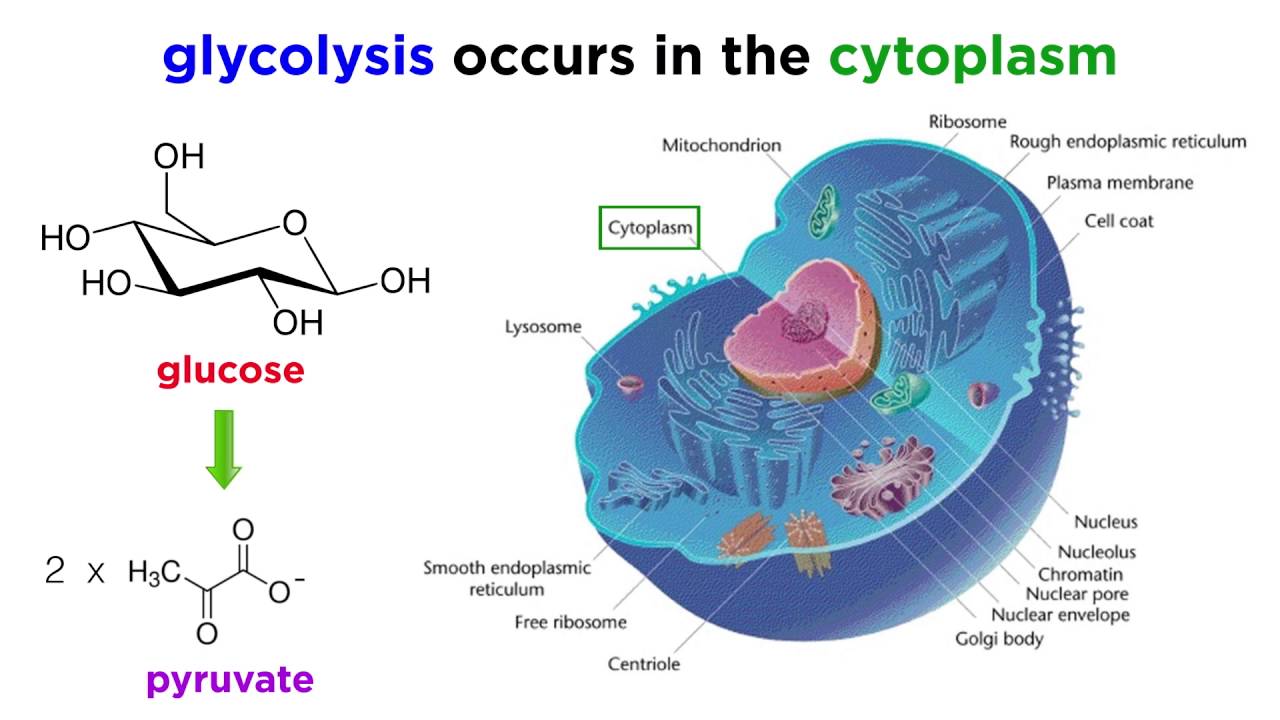
Introduction to Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell.
The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. In this process glucose is broken down in the presence of molecular oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide and much of the energy released is preserved by turning ADP and free phosphate into ATP. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration involve chemical reactions which take place in the cell to produce energy which is needed for active processes. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. Refer to the image below for a quick overview of the process taking place during this respiration.