Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

The ocean has three broad habitats.
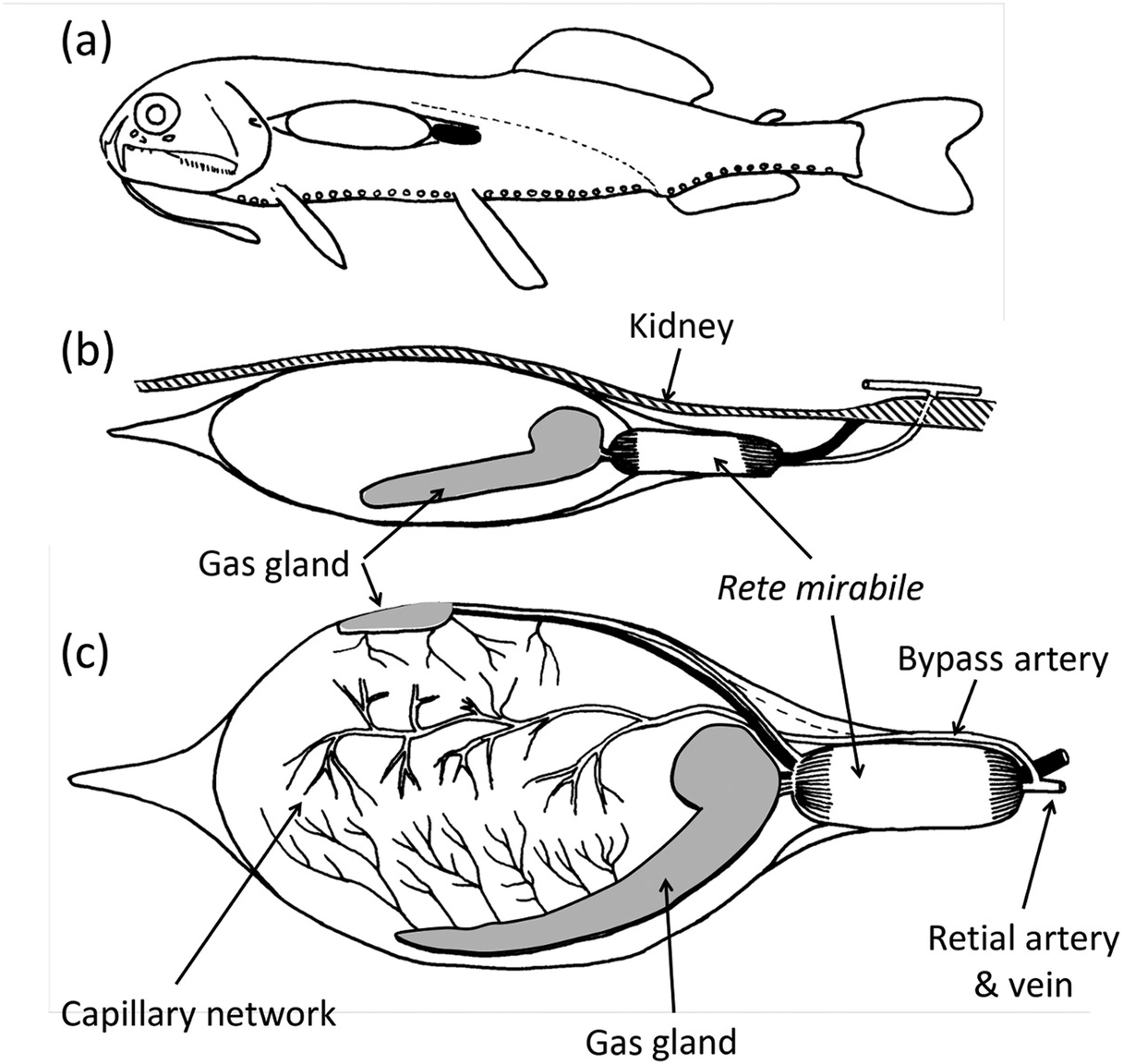
Deep ocean animals adaptations. Have students identify animal adaptations in. The photic zone also known as the sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a lake or ocean that receives sufficient sunlight to support aquatic plant life. Enzymes exhibit reduced perturbation of function by pressure membranes have fluidities adapted to deep-sea pressures and temperatures and proteins show.
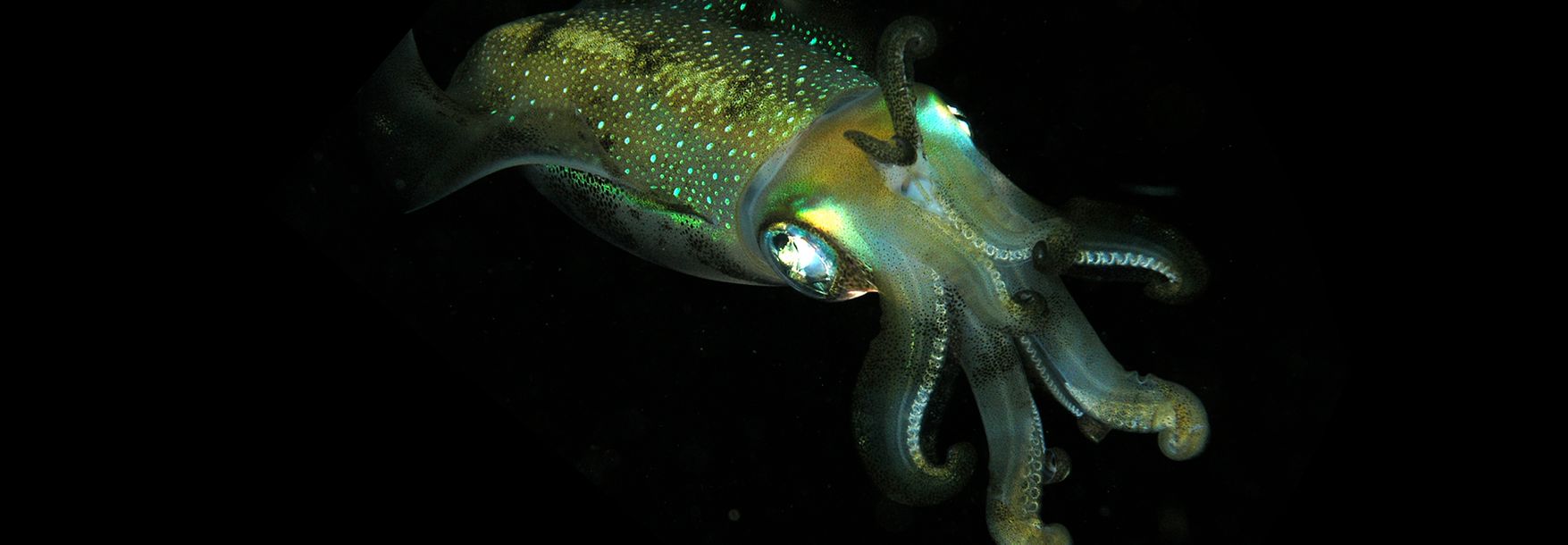
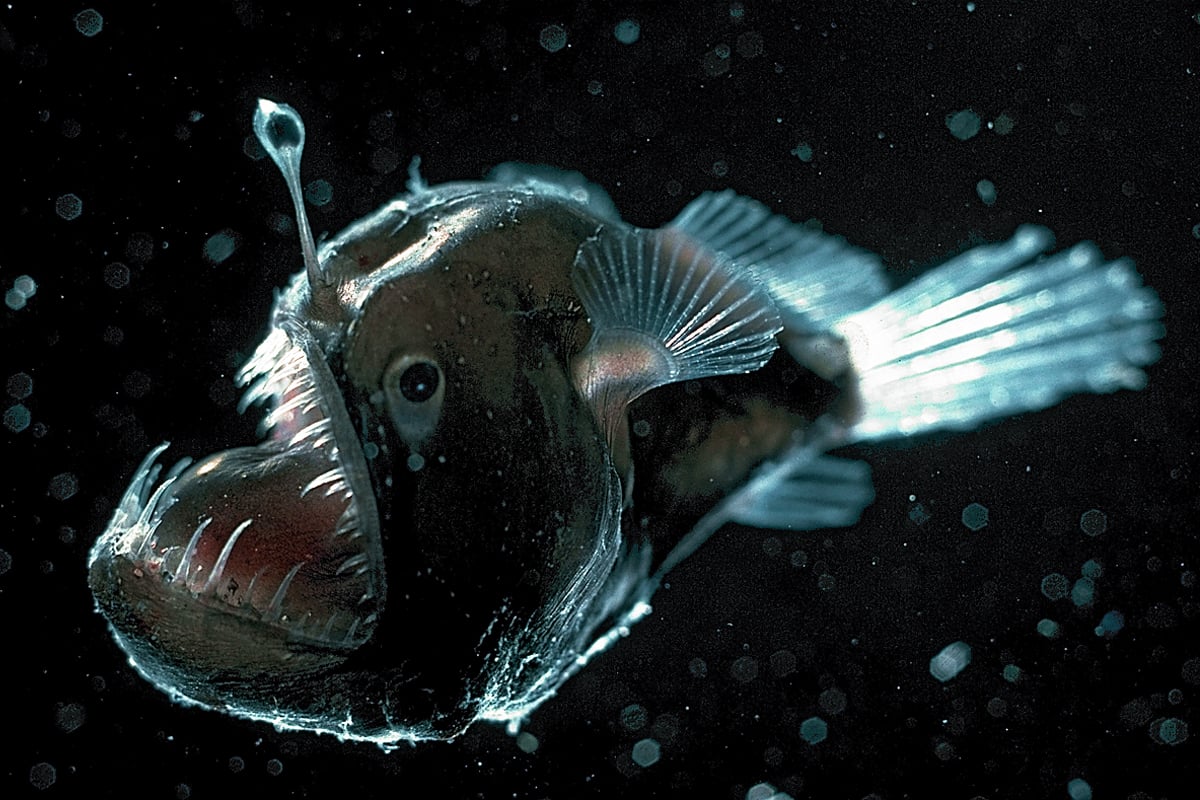
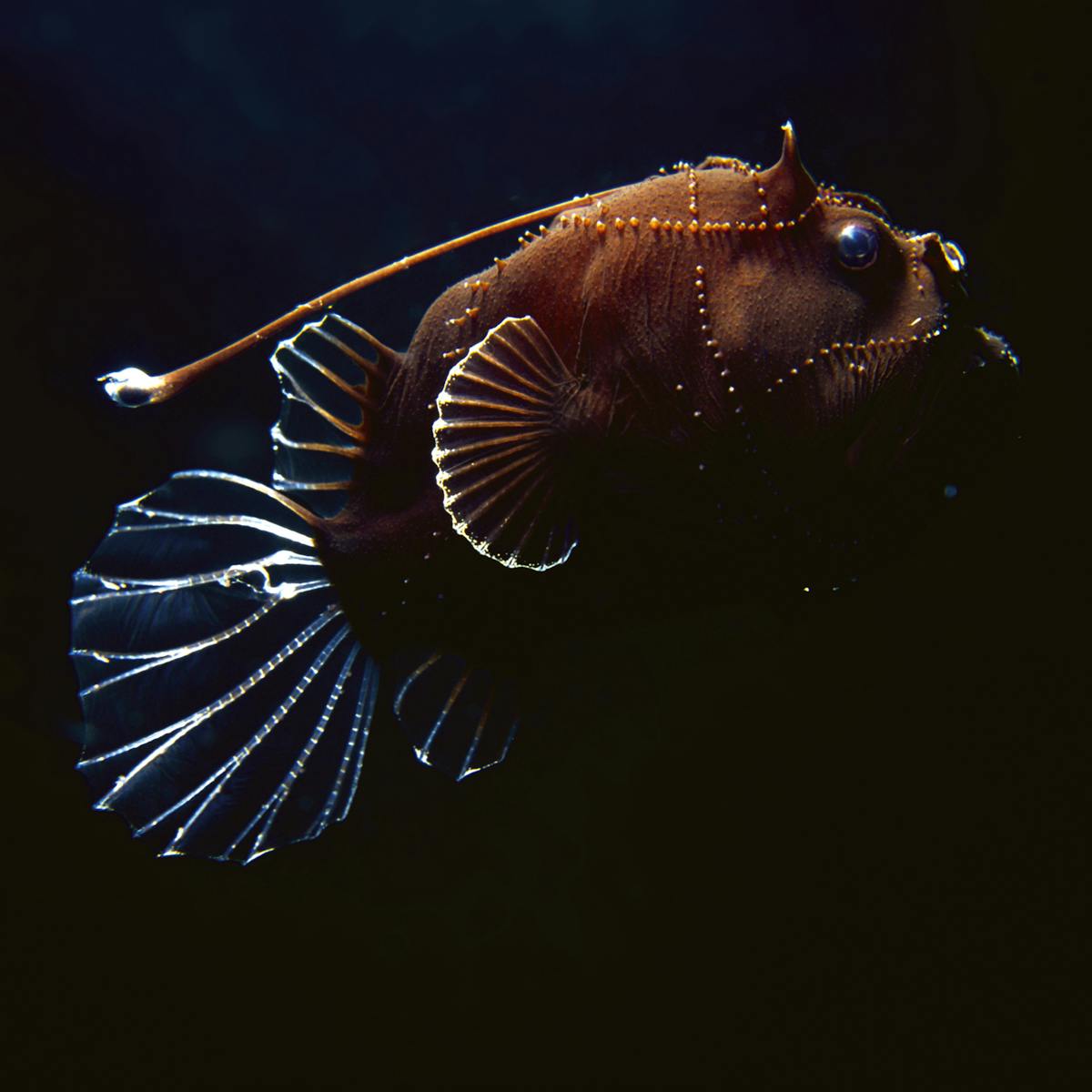
First off the deep ocean is dark because sunlight cant penetrate very far into the water. What adaptations do deep sea creatures have. Deep sea creatures have evolved some fascinating feeding mechanisms because food is scarce in these zones.
Many shellfish like. Deep-sea hot springs recently discovered along the axes of ridge and rise systems support unique communities of deep-sea animals and bacteria. Many animals such as cockles are adapted to live in these conditions.
The benthic division includes Bathyal 200 m 400 m Abyssal. Ocean animals have unique adaptations depending on what ocean habitat they. 4000 m 6000 m and Hadal from 6000 m and below zones Pelagic division includes Mesopelagic 200.
Filter feeders are oceanic animals that feed on floating organisms by straining them out of the moving water. There are several ways deep-ocean animals survive in such an environment. Deep Ocean Animal Adaptations These lessons are part of a deep ocean unit.
Deep-sea creatures are animals that live below the photic zone of the ocean. In future lessons students will research rocky shore animals to compare animals in these 2 habitats. Learn to draw deep sea fishes with interesting and surprising adaptations.