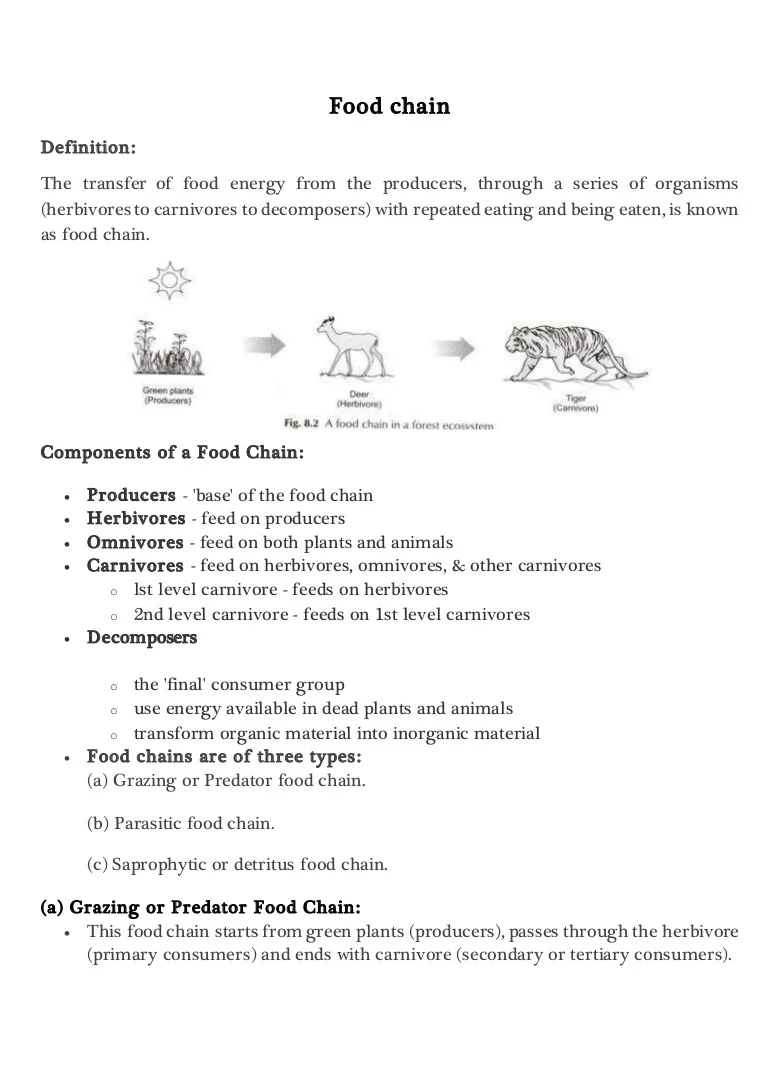
Food Chain Definition Ecology

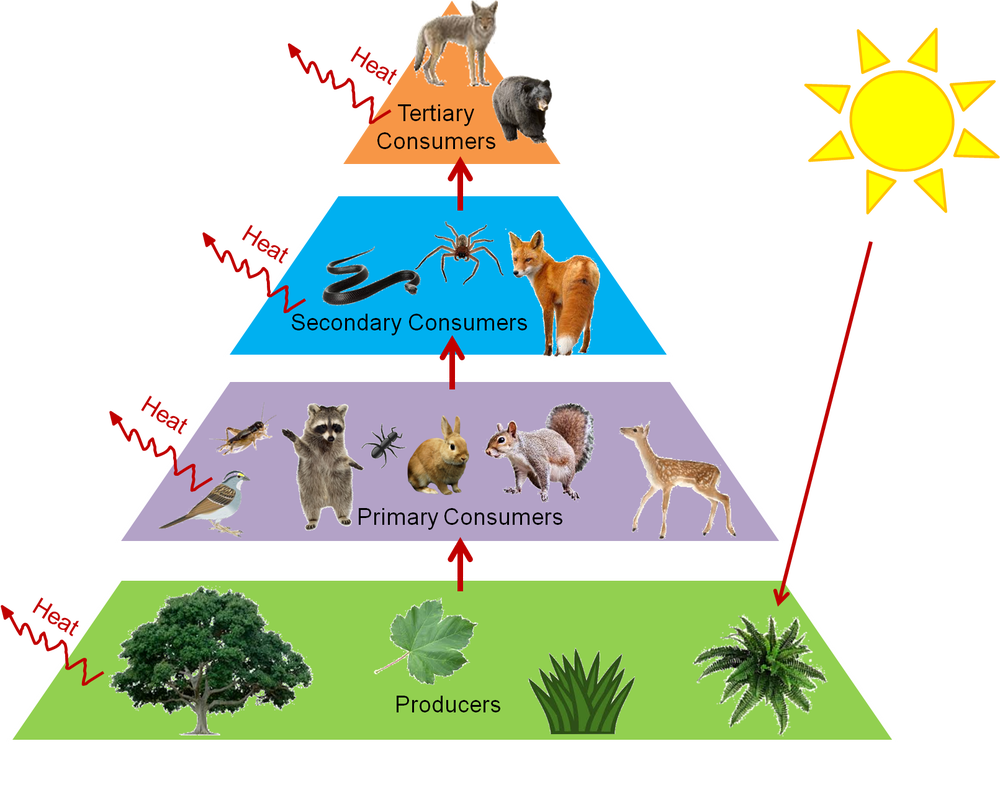
For example grass produces its own food from sunlight.
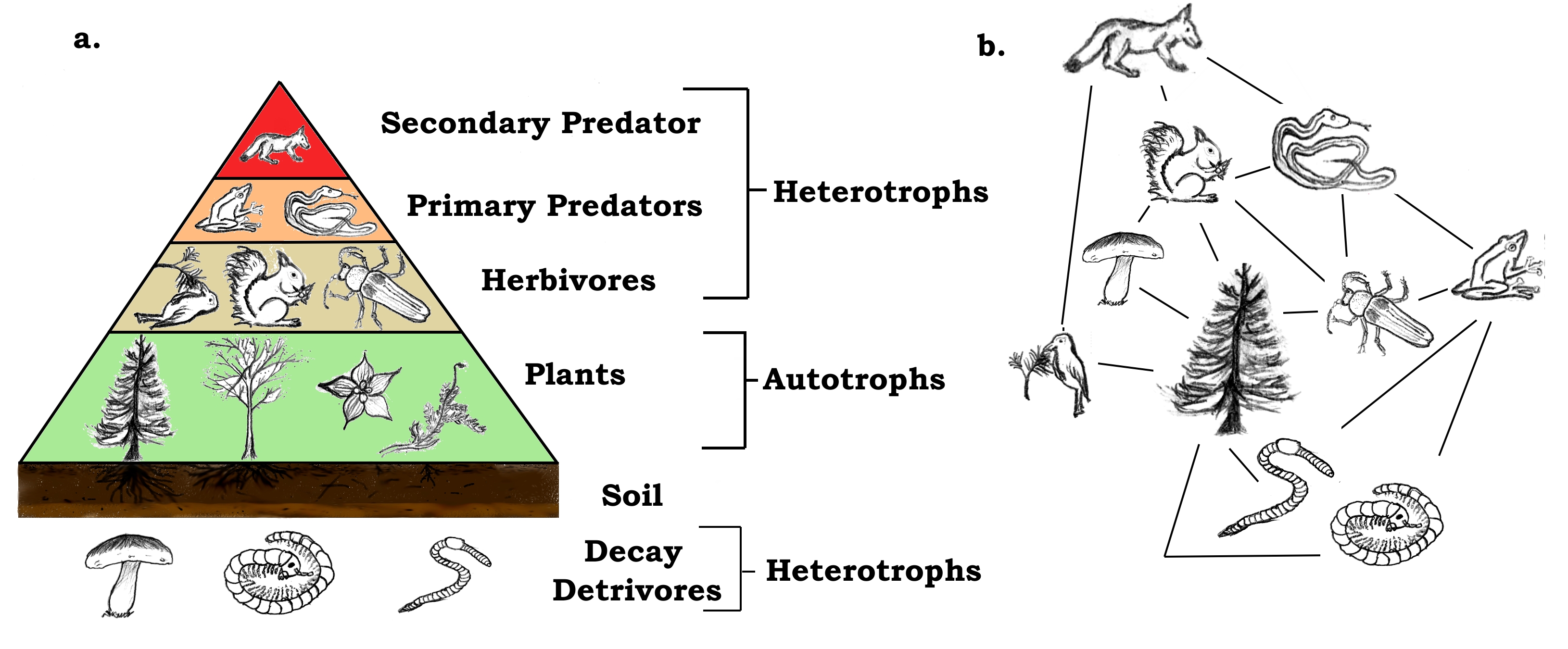
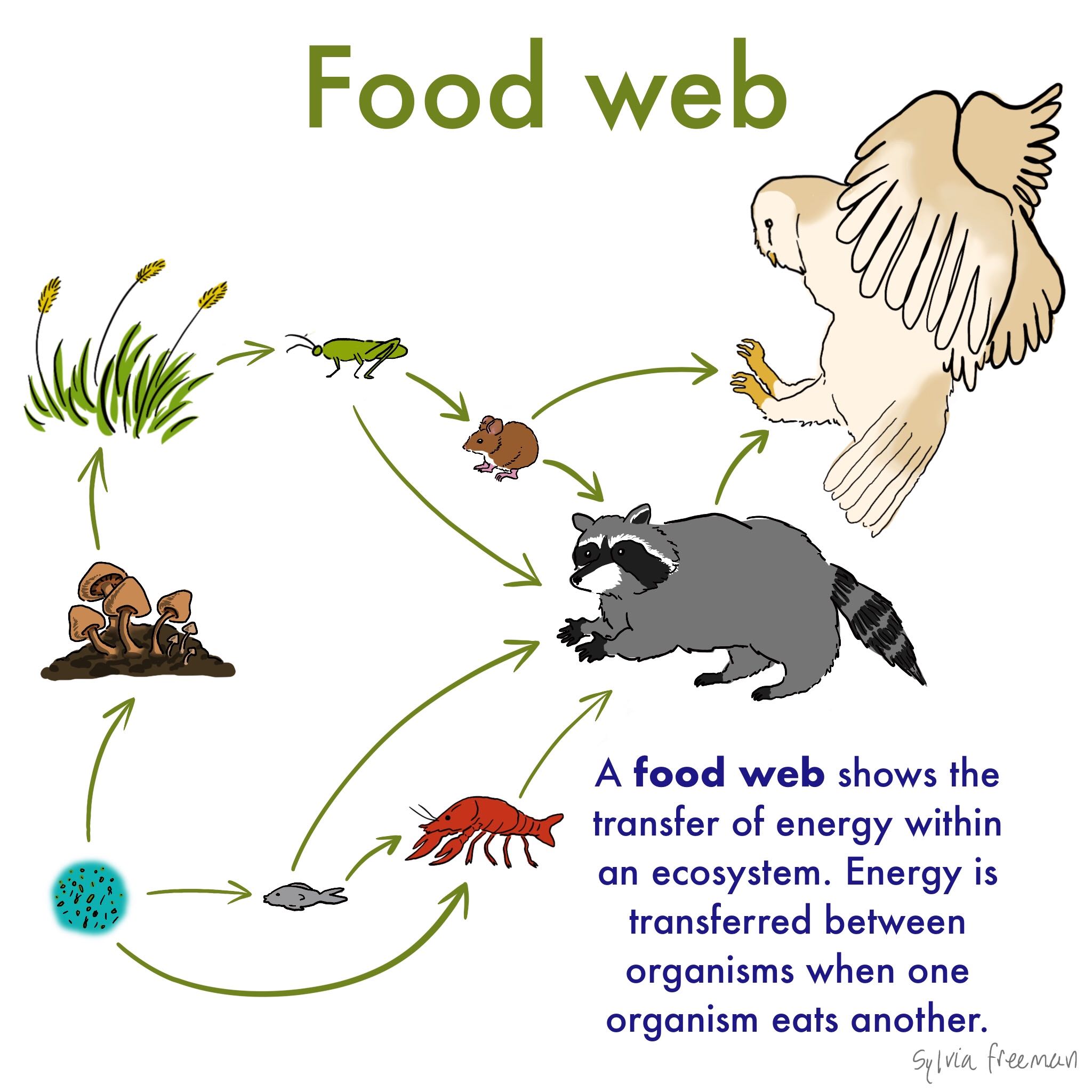
Food chain definition ecology. It shows the flow of energy and materials from one organism to the next beginning with a. This occurs when one organism consumes another organism. The producers are represented primarily by the green plants and to a lesser extent by the photosynthetic bacteria.
Food ecology is the science which looks at the food production process and assesses the impact each stage of the process has on how plants and animals relate. Video about Food Chain Definition Ecology. A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the Sun to make their food and ending at an apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaA food chain also shows how organisms are.
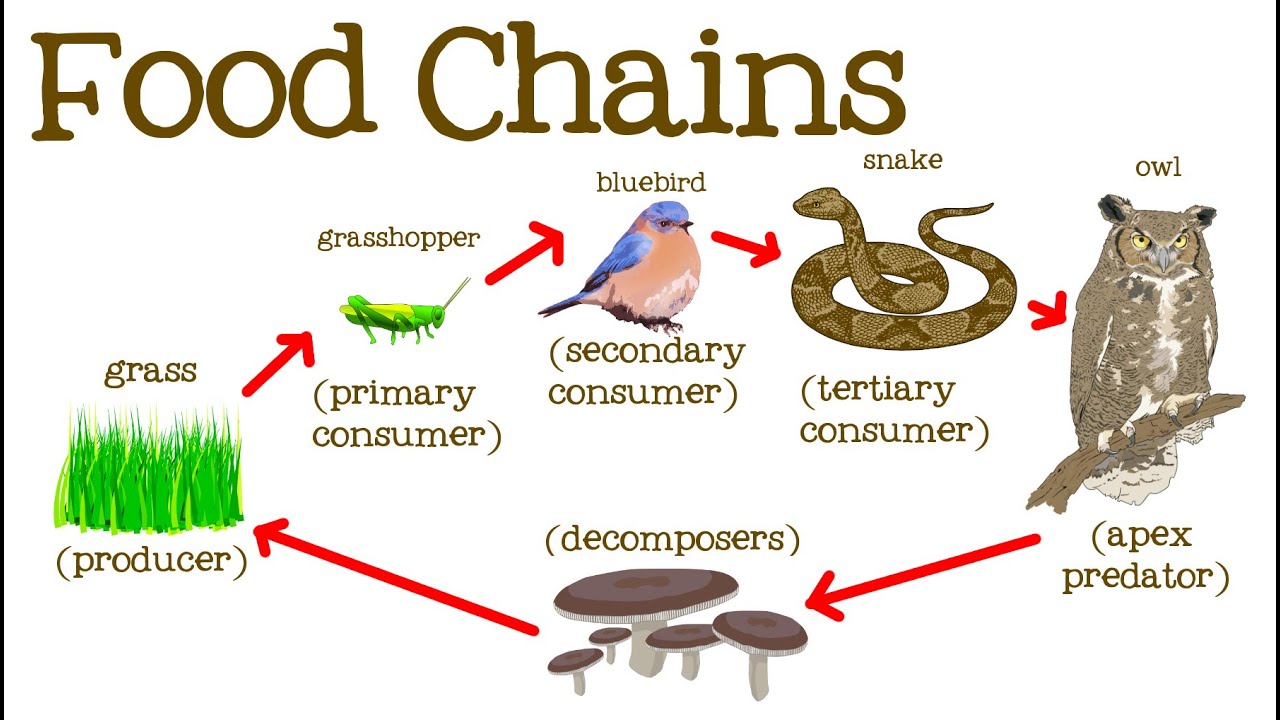
It begins with producer organism follows the chain and ends with decomposer organism. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. The term food chain describes the order in which organisms or living things depend on each other for food.
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants grasshoppers frogs snakes and hawks figure 83. Plants are eaten by insects insects are eaten by frogs the frogs are eaten by fish and fishes are eaten by humans. These easy recipes are all you need for making a delicious meal.
Every living thingfrom one-celled algae to giant blue whale sneeds food to survive. A food chain shows what eats what in a particular habitat. A food chain is basically made up of producers and consumers.
There are likely other naturalists between Linnaeus and Darwin who reported on food chains but attracted little notice. The food chain consists of four major parts. The pattern of eating and being eaten forms a linear chain called food chain.